Research project
Chemokine signaling in Tuberculosis and Salmonella infection
Who benefits from CXCR/CXCL chemokine signaling during infection: host or pathogen?
- Duration
- 2009 - 2020
- Contact
- Annemarie Meijer
- Funding
-
 European Commission 7th framework programme Grant Agreement ZF-Health
European Commission 7th framework programme Grant Agreement ZF-Health
-
 European Commission 7th framework programme Grant Agreement FishForPharma
European Commission 7th framework programme Grant Agreement FishForPharma
-
 Smart Mix Program of the Netherlands Ministry of Economic affairs and the Ministry of Education
Smart Mix Program of the Netherlands Ministry of Economic affairs and the Ministry of Education
-
 Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnólogía (CONACYT)
Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnólogía (CONACYT)
- Partners
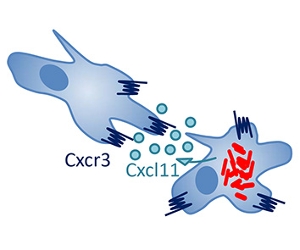
Chemokines orchestrate the migration and other functional responses of immune cells. We study the homologies between the zebrafish and human chemokine networks and use zebrafish models to study the role of evolutionary conserved chemokine signaling pathways in infectious diseases.
Pathogenic microbes such as Mycobacteria and Salmonella parasitize one on the major cell types of the innate immune system, the macrophage. These pathogens have a remarkable ability to manipulate intracellular signalling pathways, not only to subvert the macrophage defence mechanisms but also to reprogram macrophages into vectors that facilitate the dissemination into host tissues. We use zebrafish models of tuberculosis and salmonellosis to study the interaction of these pathogens with macrophages and other innate immune cells. In this project we focus on chemokine receptor-ligand signaling axes that are highly conserved between human and zebrafish, including the CXCR3/CXCL11axis and the CXCR4/CXCL12 axes. Using the tuberculosis model, we have shown that activation of these signaling axes is advantageous to the pathogen. Therefore, these pathways represent promising targets for host-directed therapeutic intervention.
- Torraca V, Masud S, Spaink HP, Meijer AH (2014) Macrophage-pathogen interactions in infectious diseases: new therapeutic insights from the zebrafish host model. Dis Mod Mech 7:785-797
- Torraca V, Cui C, Boland R, Bebelman JP, van der Sar AM, Smit MJ, Siderius M, Spaink HP, Meijer AH (2015) The CXCR3/CXCL11 signaling axis mediates macrophage recruitment and dissemination of mycobacterial infection. Dis Model Mech. 8:253-69
- Torraca V, Otto NA, Tavakoli-Tameh A, Meijer AH (2017) The inflammatory chemokine Cxcl18b exerts neutrophil-specific chemotaxis via the promiscuous chemokine receptor Cxcr2 in zebrafish. Dev Comp Immunol. 67:57-65
