Research project
The economic geography of Roman Italy
Can we identify different degrees of economic integration, both within and between regions, on the basis of archaeological proxies?
- Duration
- 2017

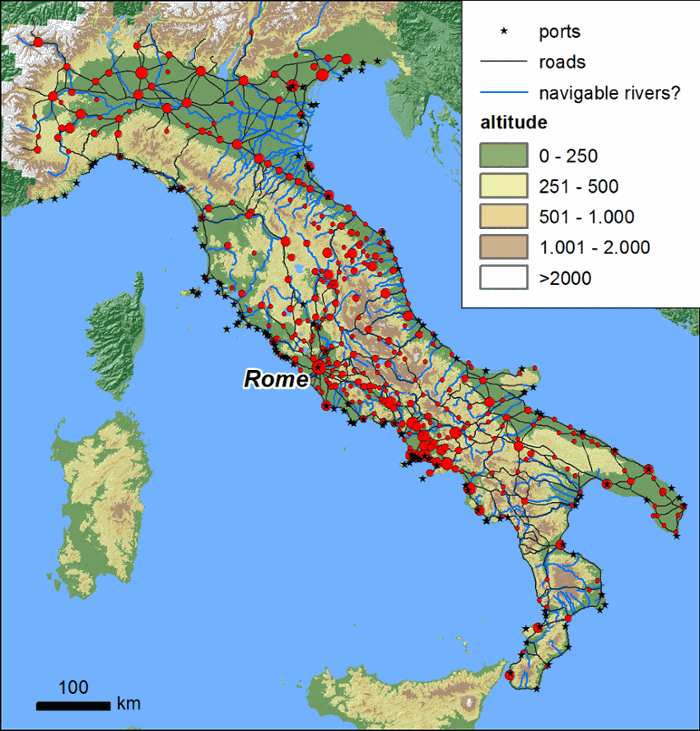
Within a previous post-doctoral research project, Dr Tymon de Haas used GIS-based spatial analysis and Network Analysis tools to investigate the geographic properties of demand and infrastructure in Roman Italy and their consequences for differential patterns of economic integration. This research showed that some regions, through demographic growth and increasingly dense infrastructural networks, had a larger potential for economic development and integration than others. However, it has so far not been established how this potential actually translates into archaeologically visible patterns of economic integration. This project therefore aims to increase our understanding of the economic geography of Roman Italy and of patterns of economic integration in particular. To explore the issue of economic integration, the project uses a multi-scalar geographic approach, applying different types of evidence and appropriate methods of analysis at the regional and supra-regional scale.
At the supra-regional scale, are there differences in the degree of integration between regions in different geographic zones? At the regional scale, are there differences in the degree of integration between different geographic zones? And if so, how do these differences relate to social and geographic factors? (e.g., are areas close to infrastructural hubs or major central places better integrated? And to what extent are not just elites, but also lower levels of society integrated?)
To answer these questions, De Haas uses both settlement and ceramic data as collected in regional field surveys and urban excavations as proxies for the extent to which sites and regions were integrated into local, regional and supra-regional economic systems.