Research project
The role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in ischaemic renal injury and regeneration
Researcher: Yu Qin
- Contact
- Bob van de Water
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced acute renal failure (ARF) shows extensive renal proximal tubular cell (PTC) injury, which is associated with the disruption of cell-extracellular matrix interactions. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions, protein complexes containing structural and signaling proteins at the interface between the cell and ECM, and is implicated in I/R induced ARF.
Homogeneous fak knockout results in FAK deficiency and early embryonic lethality. To elucidate the role of FAK in the pathophysiological process of renal I/R in vivo, we therefore use a renal PTC-specific conditional FAK knockout mouse model (gamma-GT-Cre-ERT2/FAK).
Previous data (
Alderliesten et al 2007) indicated that tamoxifen-induced conditional FAK knockout ameliorated the susceptibility of mice to I/R injury. In this follow-up study, first we will determine how FAK is involved in the activation of stress signaling (e.g. NFκB, ERK) and cell-ECM signaling pathways during ischemic injury. Second, the reperfusion period will be extended up to two weeks to investigate the effect of conditional FAK knockout on the recovery stage after ischemic injury.
We anticipate that all these studies will provide a clearer understanding of the role of FAK during renal ischemia/reperfusion process and recovery of renal tissue.
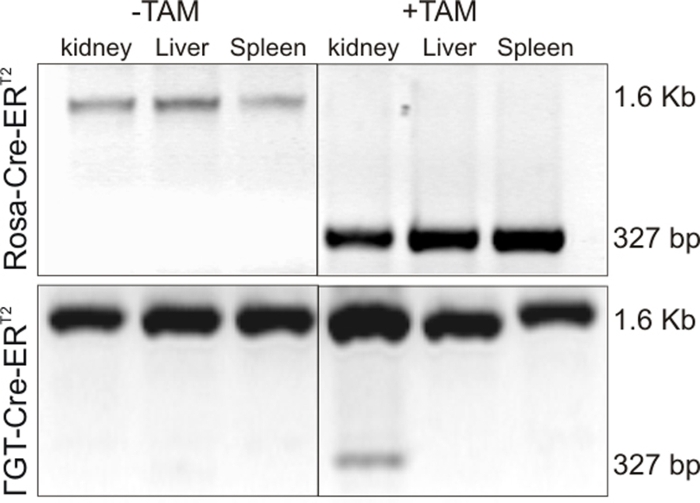
Figure 1: Tamoxifen successfully recombines loxed fak alleles in the kidney. FAKloxP/loxP//γGT-Cre-ERT2, FAKloxP/loxP//Rosa-Cre-ERT2 mice were treated with tamoxifen. 4days after the last treatment kidneys were harvested, and genomic DNA was extracted from frozen sections and checked for recombination (FAKΔloxP/ΔloxP) using a non-quantative recombination PCR.
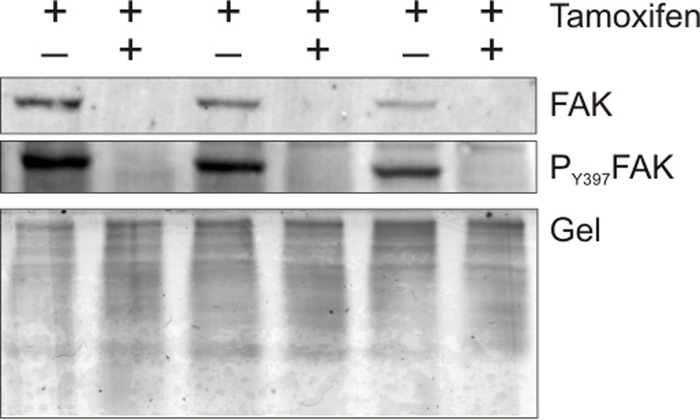
Figure 2:
FAK protein decreased in the kidneys of FAKΔloxP/ΔloxP mice.
To determine the FAK protein levels after recombination frozen sections were prepared for Western blot analysis and stained for PY397-FAK and FAK.
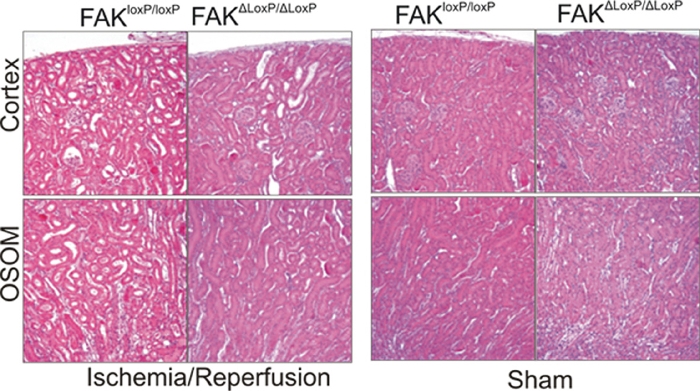
Figure 3: FAKΔloxP/ΔloxP mice are less susceptible to I/R induced injury.
FAKloxP/loxP//γGT-Cre-ERT2 mice and their FAKloxP/loxP littermates were treated with tamoxifen and then subjected to ischemia/reperfusion or sham surgery. Paraffin sections were stained for hematoxylin and eosin to determine tubular damage.
